Does Botox® Actually Work?
By Dr. Stephen Cosentino
PRESIDENT OF EMPIRE MEDICAL TRAINING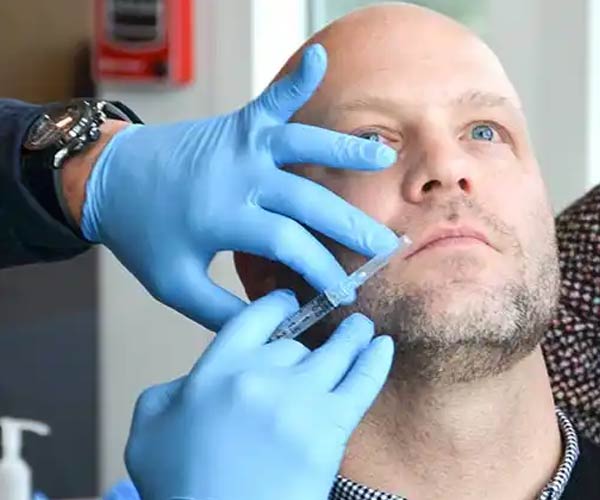
Botox® is a minimally invasive cosmetic treatment with full FDA approval to treat a range of cosmetic and medical conditions.
Every year, millions of Americans receive Botox treatments to reduce unsightly forehead lines, crow’s feet, and other types of facial lines. Many more seek Botox injections to treat medical issues that impact quality of life, such as blepharospasm (involuntary eyelid movements), bruxism (involuntary jaw clenching) and square jaw, and urinary incontinence.
Botox is regarded as safe and effective when administered by a licensed physician, dentist, or registered nurse. It’s less invasive than plastic surgery. But it’s still fair to ask whether Botox works.
The short answer is, yes, Botox works. Read on to learn how Botox works, which conditions it’s indicated to treat, and what you should know before your Botox treatment.
How Does Botox Work?
Botox injections work because of the active ingredient, botulinum toxin. Anything with “toxin” in its name sounds scary, but the truth is that medications derived from botulinum toxin are low-risk when administered in clinical doses by trained professionals, such as plastic surgeons.
Botox’s active ingredient causes muscles to contract around the injection sites. Often, these are smaller facial muscles responsible for age-related lines and wrinkles in the forehead, around the eyes and mouth, and on the cheeks. Botox also works on larger muscles in the jaw, neck, and elsewhere on the body.
Botox begins to work within days of treatment, but its effects are temporary. They last only as long as the medication remains in the body — typically three to six months but sometimes as long as 12 months. The fact that Botox is temporary is a positive thing for new patients who aren’t sure if it’s right for them, even as patients seeking sustained results generally need follow-up treatments.
What Does Botox Do?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved Botox to treat a wide variety of conditions:
- Involuntary eyelid movements (blepharospasm)
- Excessive underarm sweating
- Chronic migraine
- Urinary incontinence
- Overactive bladder
- Misaligned eyes (strabismus)
- Severe, painful neck and shoulder muscle contractions (cervical dystonia)
For anti-aging, Botox is also effective in temporarily reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles around the eyes, deeper forehead and facial wrinkles, and frown lines around the nose and mouth. While cosmetic Botox might not turn back the clock, it can absolutely smooth stubborn lines and wrinkles and leave you looking and feeling younger in the treated area.
Botox Works — But What Are the Downsides?
Botox clearly works. But does it have any downsides that patients should be aware of before seeking treatment?
Like all medications, Botox may have side effects. Most are minor and temporary. More serious, long-term complications are rare — and much less likely when you work with a licensed, trained Botox provider.
According to the National Library of Medicine, the most common potential side effects of Botox include pain, bruising, and swelling at the injection site. Less often, patients experience temporary flulike symptoms, such as headaches and muscle aches.
More concerning side effects and complications may include allergic reactions to Botox’s inactive ingredients, systemic issues like muscle weakness and urinary incontinence, and blood clotting caused by accidental injection into a blood vessel.
Always follow your Botox provider's medical advice, which may include remaining upright for a few hours after treatment and avoiding heavy physical activity until the following day. And let your provider know if you have any medical conditions or are currently taking any medications that make you a poor candidate for Botox.


